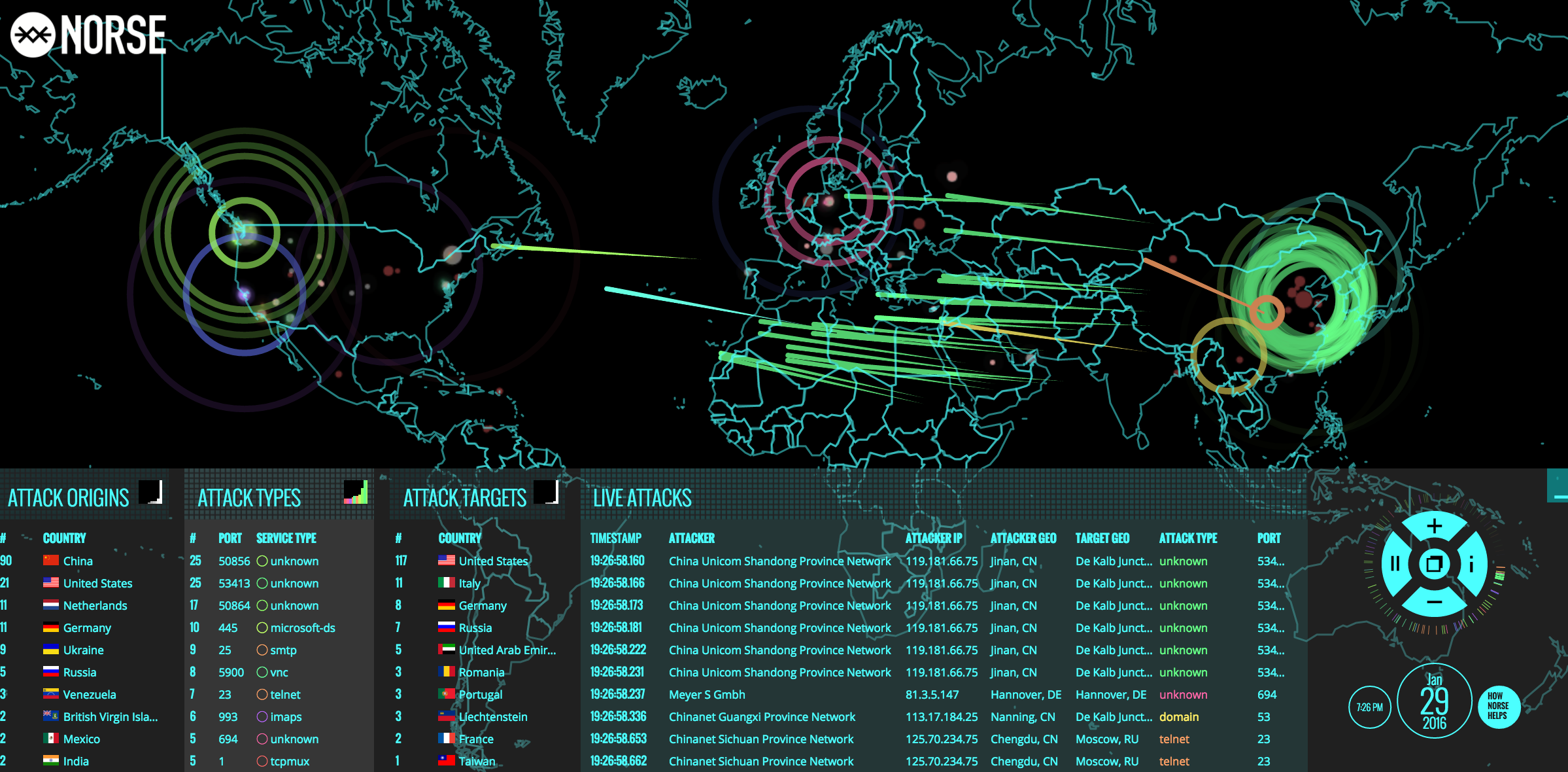
Remember Norse Corp., the company behind the interactive “pew-pew” cyber attack map shown in the image below? Norse imploded rather suddenly in 2016 following a series of managerial missteps and funding debacles. Now, the founders of Norse have launched a new company with a somewhat different vision: RedTorch, which for the past two years has marketed a mix of services to high end celebrity clients, including spying and anti-spying tools and services.
Norse’s attack map was everywhere for several years, and even became a common sight in the “brains” of corporate security operations centers worldwide. Even if the data that fueled the maps was not particularly useful, the images never failed to enthrall visitors viewing them on room-sized screens.
“In the tech-heavy, geek-speak world of cybersecurity, these sorts of infographics and maps are popular because they promise to make complicated and boring subjects accessible and sexy,” I wrote in a January 2016 story about Norse’s implosion. “And Norse’s much-vaunted interactive attack map was indeed some serious eye candy: It purported to track the source and destination of countless Internet attacks in near real-time, and showed what appeared to be multicolored fireballs continuously arcing across the globe.”
That story showed the core Norse team had a history of ambitious but ultimately failed or re-branded companies. One company proclaimed it was poised to spawn a network of cyber-related firms, but instead ended up selling cigarettes online. That company, which later came under investigation by state regulators concerned about underage smokers, later rebranded to another start-up that tried to be an online copyright cop.
Flushed with venture capital funding in 2012, Norse’s founders started hiring dozens of talented cybersecurity professionals. By 2014 it was throwing lavish parties at top Internet security conferences. It spent quite a bit of money on marketing gimmicks and costly advertising stunts, burning through millions in investment funding. In 2016, financial reality once again would catch up with the company’s leadership when Norse abruptly ceased operations and was forced to lay off most of its staff.
Now the top executives behind Norse Corp. are working on a new venture: A corporate security and investigations company called RedTorch that’s based in Woodland Hills, Calif, the home of many Hollywood celebrities.
RedTorch’s website currently displays a “We’re coming soon” placeholder page. But a version of the site that ran for two years beginning in 2018 explained what clients can expect from the company’s services:
- “Frigg Mobile Intelligence,” for helping celebrities and other wealthy clients do background checks on the people in their lives;
- “Cheetah Counter Surveillance” tools/services to help deter others from being able to spy on clients electronically;
- A “Centurion Research” tool for documenting said snooping on others.
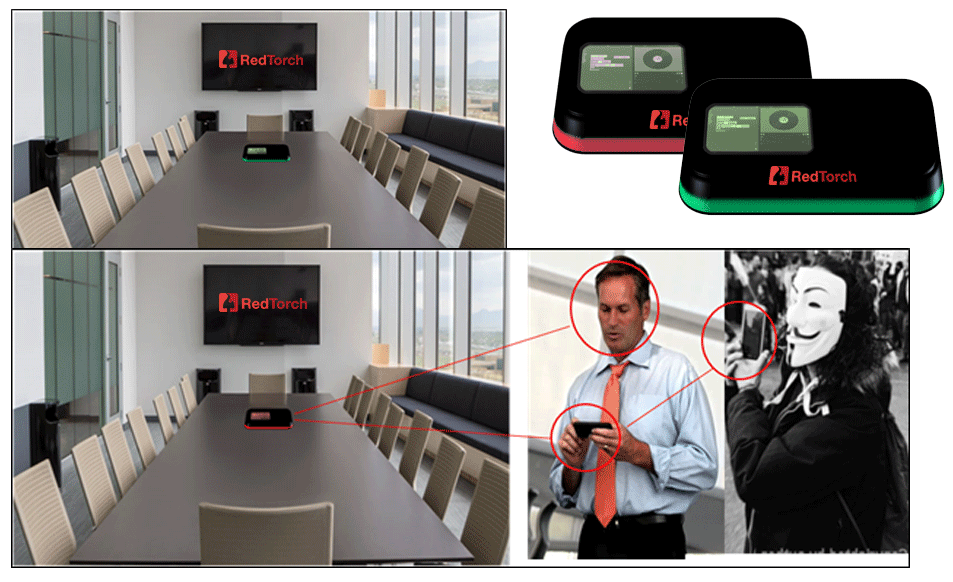

An ad for RedTorch’s “Cheetah” counter-surveillance tech. The Guy Fawkes mask/Anonymous threat featured prominently and often on RedTorch’s website.
The closest thing to eye candy for RedTorch is its Cheetah Counter Surveillance product line, a suite of hardware and software meant to be integrated into other security products which — according to RedTorch — constantly sweeps the client’s network and physical office space with proprietary technology designed to detect remote listening bugs and other spying devices.
Frigg, another core RedTorch offering, is…well, friggin’ spooky:
“Frigg is the easiest way to do a full background check and behavioral analysis on people,” the product pitch reads. “Frigg not only shows background checks, but social profiles and a person’s entire internet footprint, too. This allows one to evaluate a person’s moral fiber and ethics. Frigg employs machine learning and analytics on all known data from a subject’s footprint, delivering instant insight so you can make safer decisions, instantly.”
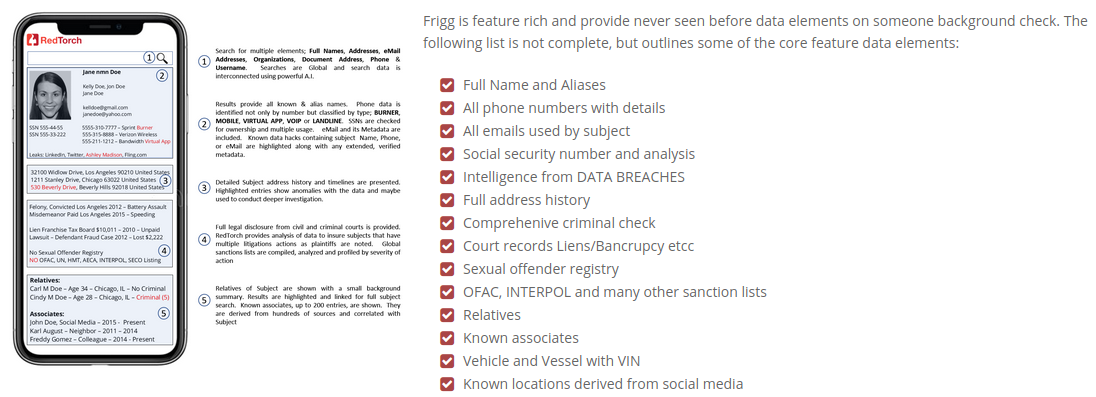
The background checking service from RedTorch, called Frigg, says it’s building “one of the world’s largest facial recognition databases and a very accurate facial recognition match standard.”
Frigg promises to include “elements that stems [sic] from major data hacks of known systems like Ashley Madison, LinkedIn, Dropbox, Fling.com, AdultFriendFinder and hundreds more. Victims of those breaches lost a lot of private data including passwords, and Frigg will help them secure their private data in the future. The matching that is shown will use email, phone and full name correlation.”
From the rest of Frigg:
Frigg references sanction lists such as OFAC, INTERPOL wanted persons, and many more international and domestic lists. Known locations results are based on social media profiles and metadata where, for example, there was an image posted that showed GPS location, or the profile mentions locations among its comments.
Frigg provides the option of continuous monitoring on searched background reports. Notification will be sent or shown once an important update or change has been detected
The flagship version of Frigg will allow a user to upload a picture of a face and get a full background check instantly. RedTorch is working to develop one of the world’s largest facial recognition databases and a very accurate facial recognition match standard.
WHO IS REDTORCH?

The co-founders of Norse Networks, “Mr. White” (left) Norse Corp. co-founder and RedTorch CEO Henry Marx;, and “Mr. Grey,” CTO and Norse Corp. co-founder Tommy Stiansen.
RedTorch claims it is building a huge facial recognition database, so it’s perhaps no surprise that its founders prefer to obscure theirs. The contact email on RedTorch says henry @retorch dot com. That address belongs to RedTorch Inc. CEO Henry Marx, a former music industry executive and co-founder of Norse Networks.
Marx did not respond to requests for comment. Nor did any of the other former Norse Corp. executives mentioned throughout this story. So I should emphasize that it’s not even clear whether the above-mentioned products and services from RedTorch actually exist.
One executive at Red Torch told this author privately that the company had plenty of high-paying clients, although that person declined to be more specific about what RedTorch might do for those clients or why the company’s site was currently in transition.
Now a cadre of former Norse Corp. employees who have been tracking the company’s past executives say they’ve peered through the playful subterfuge in the anonymous corporate identities on the archived RedTorch website.
Marx appears to be the “Mr. White” referenced in the screenshot above, taken from an archived Aug. 2020 version of RedTorch.com. He is wearing a Guy Fawkes mask, a symbol favored by the Anonymous hacker collective, the doomed man behind the failed Gunpowder plot of 1604 in England, and by possibly the most annoying costumes that darken your front door each Halloween.
Mr. White says he has “over 30 years in the entertainment industry; built numerous brands and controlled several areas of the entertainment business side,” and that he’s “accomplished over 200 million sold artist performances.”
Pictured beside Mr. White is RedTorch’s co-founder, “Mr. Grey.” Norse watchers say that would be Tommy Stiansen, the Norwegian former co-founder of Norse Corp. whose LinkedIn profile says is now chief technology officer at RedTorch. One of his earliest companies provided “operational billing solutions for telecom networks.”
“Extensive experience from Telecom industry as executive and engineer,” reads Mr. Grey’s profile at RedTorch. “Decades of Cyber security experience, entrepreneurship and growing companies; from single employee to hundreds of employees. Been active on computers since 7 years old, back in mid-80’s and have pioneered many facets of the internet and cyber security market we know today. Extensive government work experience from working with federal governments.”
Stiansen’s leadership at Norse coincided with the company’s release of a report in 2014 on Iran’s cyber prowess that was widely trounced as deeply flawed and headline-grabbing. Norse’s critics said the company’s founders had gone from selling smokes to selling smoke and mirrors.
In its report, Norse said it saw a half-million attacks on industrial control systems by Iran in the previous 24 months — a 115 percent increase in attacks! But there was just one problem: The spike in attacks Norse cited weren’t real attacks against actual industrial targets. Rather, they were against “honeypot” systems set up by Norse to mimic a broad range of devices online.
Translation: The threats Norse warned about weren’t actionable, and weren’t anything that people could use to learn about actual attack events hitting sensitive control system networks.
In a scathing analysis of Norse’s findings, critical infrastructure security expert Robert M. Lee said Norse’s claim of industrial control systems being attacked and implying it was definitively the Iranian government was disingenuous at best. Lee had obtained an advanced copy of a draft version of the Norse report that was shared with unclassified government and private industry channels, and said the data in the report simply did not support its conclusions.
Around the same time, Stiansen was reportedly telling counterparts at competing security firms that Norse had data showing that the Sony Pictures hack in November 2014 — in which Sony’s internal files and emails were published online — was in fact the work of a disgruntled insider at Sony.
Norse’s crack team of intelligence analysts had concluded that the FBI and other intelligence sources were wrong in publicly blaming the massive breach on North Korean hackers. But Norse never published that report, nor did it produce any data that might support their insider claim in the Sony hack.
Last month, the U.S. Justice Department unsealed indictments against three North Korean hackers accused of plundering and pillaging Sony Pictures, launching the WannaCry ransomware contagion of 2017, and stealing more than $200 million from banks and other victims worldwide.
Norse’s conclusions on Iran and Sony were supported by Tyson Yee, a former Army intelligence analyst who worked at Norse from 2012 to Jan. 2016. Yee is listed on LinkedIn as director of intelligence at RedTorch, and his LinkedIn profile says his work prior to RedTorch in Nov. 2018 was for two years as a “senior skunk works analyst” at an unnamed employer.